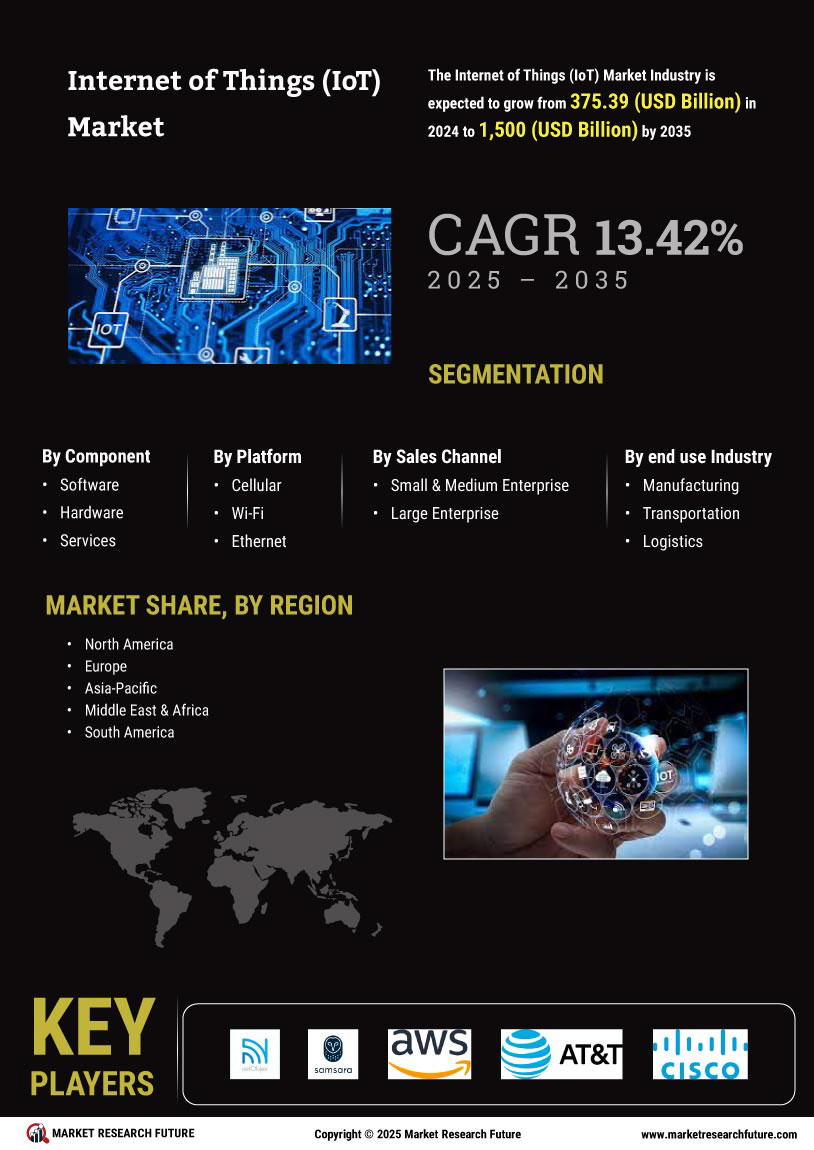
The Internet of Things (IoT): Transforming the Modern World
Introduction to IoT: Connecting Devices for a Smarter Future
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data over the internet. These devices range from everyday household items to industrial machinery, all embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. IoT aims to create smarter environments by enabling real-time data collection and analysis, leading to improved efficiency, convenience, and decision-making. As IoT devices become more affordable and accessible, they are transforming sectors like healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and home automation. This interconnected ecosystem allows devices to work collaboratively, automating tasks and providing users with valuable insights. Ultimately, IoT is shaping a future where everything is interconnected, making life more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to human needs.
How IoT Works: Components and Data Flow
IoT systems operate through a combination of sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces. Sensors collect data from the physical environment—such as temperature, motion, or humidity—and send this information via internet connectivity to centralized servers or cloud platforms. These platforms process and analyze the data, generating insights or triggering automated responses. Users can access this information through apps or control systems, enabling real-time monitoring and control. The seamless flow of data between devices and the cloud facilitates automation and predictive maintenance. Security measures, such as encryption and authentication, are essential to protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Understanding these components helps grasp how IoT creates intelligent environments that adapt and respond dynamically to changing conditions.
Applications of IoT Across Industries
IoT has vast applications across numerous industries, revolutionizing traditional practices. In healthcare, wearable devices monitor vital signs, enabling remote patient care and early diagnosis. In agriculture, IoT sensors track soil moisture and weather patterns to optimize irrigation and crop yields. Manufacturing industries utilize IoT for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Smart homes incorporate IoT devices like thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems for increased convenience and energy efficiency. Transportation benefits from IoT through connected vehicles and real-time traffic management, improving safety and reducing congestion. Retailers use IoT for inventory management and personalized customer experiences. These diverse applications demonstrate IoT’s capacity to enhance productivity, safety, and sustainability across sectors, paving the way for a more connected and intelligent world.
Challenges and Security Concerns in IoT Deployment
Despite its advantages, IoT faces significant challenges, primarily around security and privacy. The proliferation of connected devices increases the attack surface for cybercriminals, risking data breaches and system disruptions. Many IoT devices have limited security features, making them vulnerable to hacking. Privacy concerns also arise as personal data collected by IoT devices can be misused or mishandled without proper safeguards. Interoperability between diverse devices and standards remains a technical hurdle, complicating widespread deployment. Additionally, managing the massive volume of data generated requires robust infrastructure and analytical tools. Addressing these challenges involves developing stronger security protocols, establishing universal standards, and implementing privacy-by-design principles to ensure safe and reliable IoT systems that benefit users without compromising safety.
Source: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/internet-of-things-market-1176
Future Trends and the Evolution of IoT
The future of IoT promises continued growth and innovation, driven by advances in 5G, artificial intelligence, and edge computing. Faster, more reliable networks like 5G will enable real-time data processing for even more responsive IoT applications. AI integration will enhance decision-making capabilities, allowing devices to learn and adapt autonomously. Edge computing will process data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, critical for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Moreover, the development of standardized protocols and security frameworks will facilitate seamless device interoperability and safer systems.
Introduction to IoT: Connecting Devices for a Smarter Future
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data over the internet. These devices range from everyday household items to industrial machinery, all embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. IoT aims to create smarter environments by enabling real-time data collection and analysis, leading to improved efficiency, convenience, and decision-making. As IoT devices become more affordable and accessible, they are transforming sectors like healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and home automation. This interconnected ecosystem allows devices to work collaboratively, automating tasks and providing users with valuable insights. Ultimately, IoT is shaping a future where everything is interconnected, making life more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to human needs.
How IoT Works: Components and Data Flow
IoT systems operate through a combination of sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces. Sensors collect data from the physical environment—such as temperature, motion, or humidity—and send this information via internet connectivity to centralized servers or cloud platforms. These platforms process and analyze the data, generating insights or triggering automated responses. Users can access this information through apps or control systems, enabling real-time monitoring and control. The seamless flow of data between devices and the cloud facilitates automation and predictive maintenance. Security measures, such as encryption and authentication, are essential to protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Understanding these components helps grasp how IoT creates intelligent environments that adapt and respond dynamically to changing conditions.
Applications of IoT Across Industries
IoT has vast applications across numerous industries, revolutionizing traditional practices. In healthcare, wearable devices monitor vital signs, enabling remote patient care and early diagnosis. In agriculture, IoT sensors track soil moisture and weather patterns to optimize irrigation and crop yields. Manufacturing industries utilize IoT for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Smart homes incorporate IoT devices like thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems for increased convenience and energy efficiency. Transportation benefits from IoT through connected vehicles and real-time traffic management, improving safety and reducing congestion. Retailers use IoT for inventory management and personalized customer experiences. These diverse applications demonstrate IoT’s capacity to enhance productivity, safety, and sustainability across sectors, paving the way for a more connected and intelligent world.
Challenges and Security Concerns in IoT Deployment
Despite its advantages, IoT faces significant challenges, primarily around security and privacy. The proliferation of connected devices increases the attack surface for cybercriminals, risking data breaches and system disruptions. Many IoT devices have limited security features, making them vulnerable to hacking. Privacy concerns also arise as personal data collected by IoT devices can be misused or mishandled without proper safeguards. Interoperability between diverse devices and standards remains a technical hurdle, complicating widespread deployment. Additionally, managing the massive volume of data generated requires robust infrastructure and analytical tools. Addressing these challenges involves developing stronger security protocols, establishing universal standards, and implementing privacy-by-design principles to ensure safe and reliable IoT systems that benefit users without compromising safety.
Source: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/internet-of-things-market-1176
Future Trends and the Evolution of IoT
The future of IoT promises continued growth and innovation, driven by advances in 5G, artificial intelligence, and edge computing. Faster, more reliable networks like 5G will enable real-time data processing for even more responsive IoT applications. AI integration will enhance decision-making capabilities, allowing devices to learn and adapt autonomously. Edge computing will process data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, critical for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Moreover, the development of standardized protocols and security frameworks will facilitate seamless device interoperability and safer systems.
The Internet of Things (IoT): Transforming the Modern World
Introduction to IoT: Connecting Devices for a Smarter Future
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data over the internet. These devices range from everyday household items to industrial machinery, all embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. IoT aims to create smarter environments by enabling real-time data collection and analysis, leading to improved efficiency, convenience, and decision-making. As IoT devices become more affordable and accessible, they are transforming sectors like healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and home automation. This interconnected ecosystem allows devices to work collaboratively, automating tasks and providing users with valuable insights. Ultimately, IoT is shaping a future where everything is interconnected, making life more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to human needs.
How IoT Works: Components and Data Flow
IoT systems operate through a combination of sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces. Sensors collect data from the physical environment—such as temperature, motion, or humidity—and send this information via internet connectivity to centralized servers or cloud platforms. These platforms process and analyze the data, generating insights or triggering automated responses. Users can access this information through apps or control systems, enabling real-time monitoring and control. The seamless flow of data between devices and the cloud facilitates automation and predictive maintenance. Security measures, such as encryption and authentication, are essential to protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Understanding these components helps grasp how IoT creates intelligent environments that adapt and respond dynamically to changing conditions.
Applications of IoT Across Industries
IoT has vast applications across numerous industries, revolutionizing traditional practices. In healthcare, wearable devices monitor vital signs, enabling remote patient care and early diagnosis. In agriculture, IoT sensors track soil moisture and weather patterns to optimize irrigation and crop yields. Manufacturing industries utilize IoT for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Smart homes incorporate IoT devices like thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems for increased convenience and energy efficiency. Transportation benefits from IoT through connected vehicles and real-time traffic management, improving safety and reducing congestion. Retailers use IoT for inventory management and personalized customer experiences. These diverse applications demonstrate IoT’s capacity to enhance productivity, safety, and sustainability across sectors, paving the way for a more connected and intelligent world.
Challenges and Security Concerns in IoT Deployment
Despite its advantages, IoT faces significant challenges, primarily around security and privacy. The proliferation of connected devices increases the attack surface for cybercriminals, risking data breaches and system disruptions. Many IoT devices have limited security features, making them vulnerable to hacking. Privacy concerns also arise as personal data collected by IoT devices can be misused or mishandled without proper safeguards. Interoperability between diverse devices and standards remains a technical hurdle, complicating widespread deployment. Additionally, managing the massive volume of data generated requires robust infrastructure and analytical tools. Addressing these challenges involves developing stronger security protocols, establishing universal standards, and implementing privacy-by-design principles to ensure safe and reliable IoT systems that benefit users without compromising safety.
Source: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/internet-of-things-market-1176
Future Trends and the Evolution of IoT
The future of IoT promises continued growth and innovation, driven by advances in 5G, artificial intelligence, and edge computing. Faster, more reliable networks like 5G will enable real-time data processing for even more responsive IoT applications. AI integration will enhance decision-making capabilities, allowing devices to learn and adapt autonomously. Edge computing will process data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, critical for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Moreover, the development of standardized protocols and security frameworks will facilitate seamless device interoperability and safer systems.
0 Comentários
0 Compartilhamentos
1KB Visualizações
0 Anterior