Complex Mechanism Integration in Anti-theft Container Mould Systems
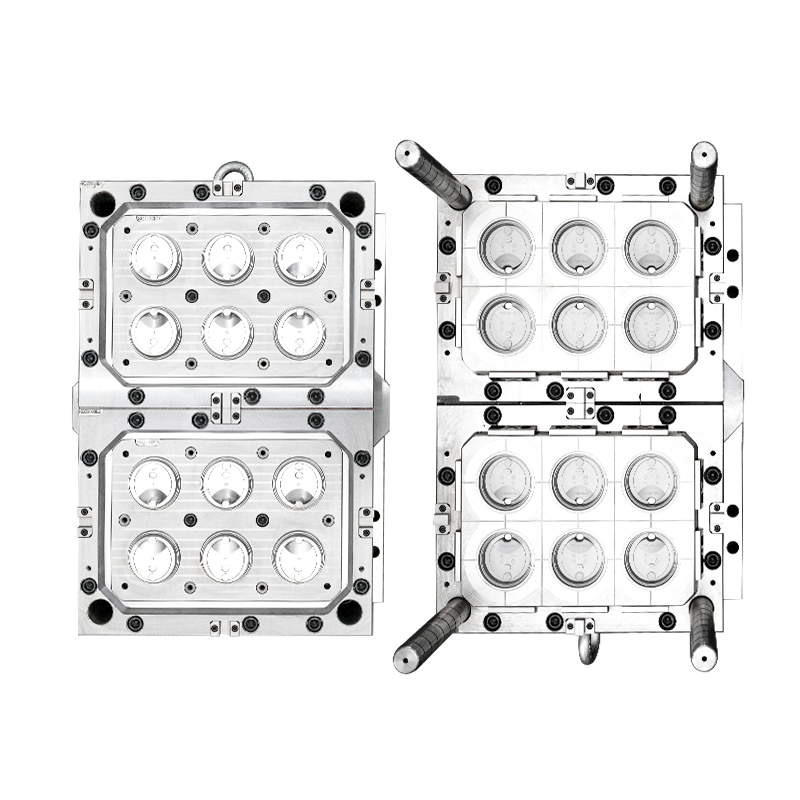
The functional requirements of an anti-theft structure container injection mould necessitate innovative approaches to mould mechanics that extend beyond conventional tooling designs. This specialized category of container injection mould incorporates moving components that create the geometrical complexities required for tamper-resistant features. The mould structure must facilitate the formation of internal undercuts, interlocking channels, and directional assemblies that would be impossible to produce with standard tooling approaches. The design philosophy for such an injection mould prioritizes the reliable operation of these mechanical systems cycle after cycle, while maintaining the precise tolerances necessary for security performance. The initial mould design phase involves extensive simulation of both plastic flow and mechanical movement to identify potential conflicts before tool manufacturing begins. This proactive engineering approach ensures that the complex mould structure will function cohesively when implemented in production environments, creating a container that meets both security and manufacturing requirements.
Slider mechanisms represent a fundamental component in many anti-theft structure container injection mould designs, enabling the formation of external security features and lateral undercuts. These sliders move perpendicular to the mould opening direction, operated by angled pins that convert vertical platen movement into horizontal slider motion. In a sophisticated container injection mould, multiple sliders may work in concert to create complex geometrical features that shield access points or create concealed locking mechanisms. The mould design must ensure that these sliders move with synchronized precision and maintain proper sealing against the main mould cavity to prevent plastic leakage. Lifter mechanisms serve a similar purpose for internal undercuts, moving at an angle to simultaneously form and release features that would otherwise trap the plastic part on the mould core. The integration of these components transforms a static mould structure into a dynamic system capable of creating the sophisticated geometries required for anti-theft functionality.
Ejection considerations present unique challenges in an anti-theft structure container injection mould due to the fragile nature of some security features and the general complexity of the parts. A standard ejection system with simple pins may be insufficient or could damage delicate components during the stripping process. The mould design often incorporates specialized ejection techniques such as sleeve ejectors, blade ejectors, or stripper plates that provide balanced, simultaneous release from multiple contact points. The ejection system must work in harmony with the sliders and lifters, with carefully sequenced movements to prevent collision or interference. The mould structure typically includes advanced sensors that verify the complete retraction of all moving components before the mould closes for the next cycle, preventing damage to the expensive tooling. This integrated systems approach to ejection ensures that each container is released without stress marks, deformation, or other damage that might compromise either the security features or cosmetic appearance.
Cooling system implementation requires innovative thinking in an anti-theft structure container injection mould due to space limitations created by the numerous moving components. The network of channels that circulate temperature-controlled fluid must navigate around slider housings, lifter guides, and other mechanical elements within the constrained space of the mould structure. This often necessitates the use of conformal cooling channels that follow the contours of the mould cavity more precisely than traditional drilled passages. These complex channels provide more uniform heat extraction, reducing cycle times while improving part quality by minimizing differential shrinkage and warpage. The mould design may also incorporate baffles, bubblers, or thermal pins to direct cooling to areas that are otherwise inaccessible. A properly engineered cooling system ensures consistent thermal conditions throughout the injection mould, which is essential for maintaining the dimensional stability of the security features formed in the mould cavity. This thermal management extends the tool life by reducing thermal stress on the mould structure components, protecting the investment in this sophisticated manufacturing asset.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


